Introduction
It’s the Sherlock Holmes of the data world, a silent detective unraveling the mysteries that lie behind each strand of data. But why should we care about it? Because understanding data lineage – the source, relationships, and transformations of your data – is like having your own Watson in the complex world of analytics.
Picture it like a breadcrumb trail in a forest – but instead of leading us out, it guides us deeper. Deeper into the origin and transformation of our data, enabling us to trace and audit our information flow and maintain data integrity. In doing so, it saves us from wandering lost in the ‘wild forest’ of erroneous analysis, mistrust, and ultimately, poor decision-making.
Consider this your comprehensive map to the world of data lineage. Here, we don’t just explore what it is, but also why it’s critical for your organization, and how implementing it can chart your route to insightful and trustworthy data.
Unraveling the Importance of Data Lineage
- Grasp the definition and relevance of data lineage
- Illuminate why every business needs to prioritize it
- Cement how it entrenches itself in data management practices
Understanding the concept and components of data lineage
Data lineage can be likened to a life-cycle, mapping the journey of any data element right from its origin to the series of transformations it undergoes throughout its life. It gives a birds-eye view of what influences the data, how it mutates, and how we arrive at the final data point. Manifesting as a comprehensive map, data lineage acts as a navigator, steering through the maze of data’s origin, its passage, and modifications.
Data lineage as a genealogy tree would have roots branching out to different sets of data, each branch signifying a transformation or process the data has gone through. The meticulous tracking, much like a breadcrumb trail, illuminates how the data has evolved. With intricate details such as where the data was extracted from, the processes it undertook, and its form at every stage of transformation – it indeed makes the data’s lineage a lighthouse for big data landscapes.
Here is a breakdown of its components::
Sources
The original sources of data could include databases, files, applications, APIs, or external systems. They are the starting points for data lineage tracking.
Transformations
These transformations include data cleaning, aggregation, filtering, merging, or any other operation that alters the original data. Each transformation must be documented to understand how the data has changed over time.
Flow
Data flows through different systems, applications, and processes within an organization. Data lineage captures the flow of data, highlighting the movement from one system to another, ensuring transparency and visibility into the data’s path.
Dependencies
Data lineage also captures the dependencies between different data elements. It helps identify which data elements are derived from others, enabling a clear understanding of the relationships and impacts within the data ecosystem.
Good data, bad data – the outcome hinges on a business’s understanding of its data’s genesis. Often hand in hand with data quality, data integrity, and data governance – data lineage takes center stage, ascertaining data accuracy and trustworthiness.
Imagine, for a moment, an errant data point detected in a report. Without data lineage, correcting that discrepancy would be like trying to find a needle in a haystack. But with data lineage mapping the data, its metamorphosis from raw to processed, pinning down the culprit becomes a breeze – a forensics team at the crime scene if you may.
Data lineage doesn’t just locate the error, it empowers businesses with the means to amend it. By charting out the entire data journey, it equips businesses with insights to enhance decision-making processes, facilitating an advanced understanding of data flows, ensuring regulatory compliance, and fostering trust with stakeholders. It’s not just a best practice, but a business imperative.
The role of data lineage in data management
Swimming amidst a sea of data, data lineage serves as the compass that directs data management initiatives. Data lineage fundamentally simplifies data tracing, monitoring, and auditing – proving invaluable in maintaining data integrity and enforcing data governance.
Let’s look at a business rolling out a new data-centric project for instance. Implementing data lineage at the outset presents a concrete understanding of data sources and its travel itinerary – reducing the risk of operational inefficiencies and potent discrepancies down the line. It serves as rigorous documentation easing change management and providing a safety net against data corruption.
In essence, data lineage fuels a proactive rather than reactive data management strategy. It doesn’t just put out fires, but identifies the potential sparks – making it indispensable in a dynamic data management framework.
Exploring Data Lineage Tools
- Discover what data lineage tools are
- Understand how data lineage tools function
- Identify top data lineage software available
Introduction to Data Lineage Tools
A good data lineage tool doesn’t just reveal your data’s life history – it helps you understand your data’s credibility, authenticity and reliability. Integration with data lineage tools is now becoming a business necessity, enabling organizations to ensure compliance, optimize operations and make data-driven decisions with confidence.
How Data Lineage Tools Work
Data lineage tools operate on a surprisingly simple principle: they track, capture, and visualize every interaction between your data and your systems. From the moment of inception, every change, use, or transformation is logged. The data lineage tool then gives you a complete, visual map of your data’s journey, often in real time. This enables you to query the data at any point in its lifecycle, assess its integrity, and understand its context.
Top Data Lineage Tools in the Market
As a company specializing in data modernization and management, we align ourselves with the finest technology partners in the industry, leveraging top-tier data lineage tools. These partnerships are integral to our strategy, enhancing our ability to help organizations navigate their data’s lifecycle with precision and insight.
Talend
Talend, famed for its open-source platform, offers an accessible data lineage tool within its Talend Data Fabric product. It enables mapping and governance of data across a wide range of environments and formats, ensuring that users can maintain control and visibility over their data landscape.
Collibra
Collibra has emerged as a leader in data governance and cataloging, providing tools that empower organizations to understand, govern, and leverage their data to its fullest potential. Its focus is on facilitating easy access to trusted data. It’s uniquely designed to simplify the tracing of data from its origin through its transformations, securing its place as a vital tool for organizations aiming to ensure data integrity and leverage their information assets strategically. Collibra’s approach to data lineage empowers businesses with the clarity and control needed to navigate complex data environments confidently.
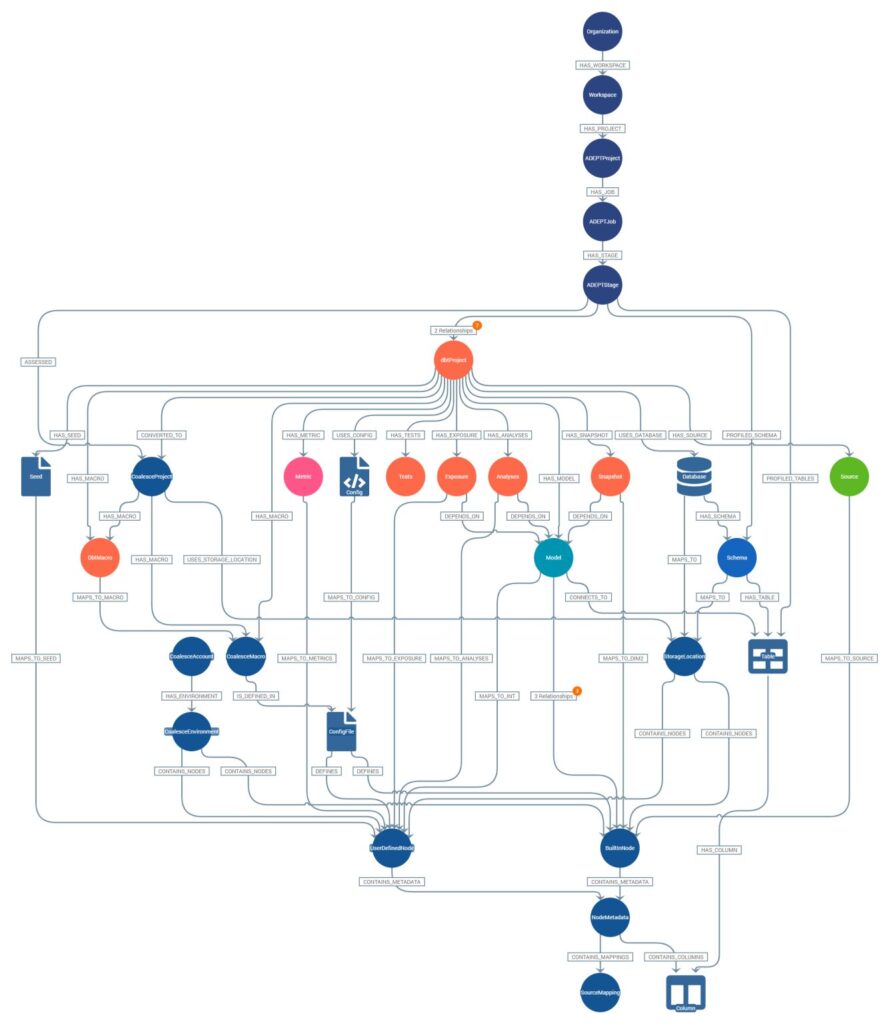
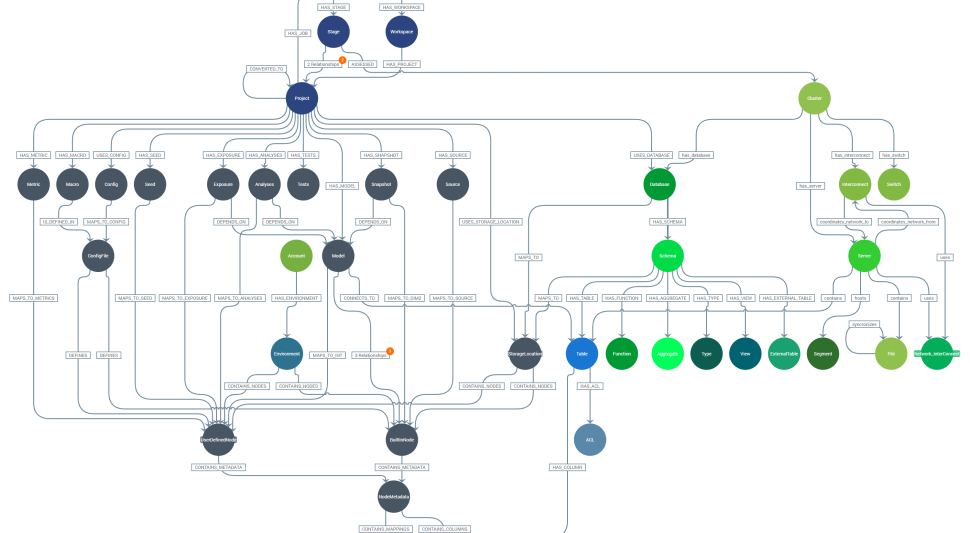
Our metadata-driven toolkit, ADEPT, offers lineage analysis and comprehensive assessments. Users can trace and understand the connections between SQL scripts and other assets within their tech stack. It also enables us to build custom connectors to bridge the gap between different technologies.
This toolkit was born out of practical experience and is designed to tackle real-world challenges in client environments. ADEPT excels in lineage analysis, offering users the ability to trace and comprehend the intricate connections between SQL scripts and various assets within their technology stack. A notable innovation is our ability to create custom connectors, seamlessly bridging disparate technologies. A prime example of this is our unique connector, Talend DQ to Collibra, the only one of its kind, enabling us to enhance the platforms and data governance capabilities of our technology partners through unrivaled integration and functionality.
To learn more about our unique connector, request for a custom connector or explore how ADEPT can elevate your data management strategy, reach out to us. Request a Demo or Inquire Further.
By implementing and utilizing data lineage tools, businesses are more equipped to handle complex data processes, enhancing efficiency and catalyzing informed decision-making. An informed choice on the right data lineage tool, therefore, is an investment toward better business outcomes. Use this understanding to guide your exploration of other key data management concepts.
The Connection between Data Governance and Data Lineage
- Grasp the fundamentals of data governance
- Understand how data lineage augments data governance
- Learn from a success story of a positive integration of data governance with data lineage
Defining Data Governance
Data governance forms a critical layer of control in the vast landscape of information management. It defines a framework for decision rights and responsibilities concerning an organization’s data assets. So, it’s pivotal in managing the quality, consistency, and security of your data, dramatically stepping up its business value. It underpins an umbrella approach to handle various aspects—data architecture, integration, and operation, among others.
With an efficient data governance strategy in place, enterprises can ensure that their data is precise, trusted, and secure. Consequently, aiding them in making more informed business decisions, mitigating data-related risks, and promoting operational effectiveness. Simultaneously, it can help in compliance with data-related regulations and standards. Making data governance an inevitable part of your organization’s strategic outlook.
So where does data lineage come into play?
How Data Lineage Supports Data Governance
Data lineage serves as an ideal enabler for data governance. It offers an auditable record of the data journey—origin, movement, what happens to it, and where it ends up in an organization. Hence, amplifying transparency, accuracy, and accountability, all essential constituents of robust data governance.
When integrated into the data governance structure, data lineage can aid in reinforcing data quality, identifying redundancies, and fostering regulatory compliance. It can provide an easier audit process, unravel the path for data errors or exceptions, and importantly, lends technical metadata for data stewards. It transforms data governance from just a strategic obligation to an accurately actionable process.
To better comprehend the integral role of data lineage in data governance, let’s examine a real-world case.
Case Study: Successful Implementation of Data Governance with Data Lineage
A leading bank that implemented a solid data governance structure using data lineage for improved understanding. The bank struggled with data accuracy, regulatory compliance, and risk management issues. Then, they introduced a data governance unit and implemented data lineage tools as part of their overall data strategy.
Data lineage tools helped them effectively track data lifecycle, enhancing transparency, data trust, and operational efficiency. In addition, it simplified the complex audit processes, ensuring precise reports and improved stakeholder communication.
The integration of data lineage resulted in significant improvement in data quality, regulatory compliance, and risk management. The bank continues to leverage this for informed decision-making processes and to stay ahead in the competitive marketplace. This is an example of how data lineage amplifies the critical role data lineage can play in ramping up data governance.
So, data governance and data lineage aren’t isolated entities but closely intertwined that together deliver a powerful data strategy for your enterprise. Data governance is covered here in more detail.
Data Lineage in Business Intelligence
- Profound understanding of data lineage as a game-changer in business intelligence
- Identifying how data lineage expedites accurate decision-making
- Learn from a practical scenario: harnessing data lineage in business intelligence
The Role of Data Lineage in Business Intelligence
Data Lineage lays out a detailed map of your valuable data journey, from where it originates to the transformation processes it undergoes. In the sphere of Business Intelligence (BI), it plays an instrumental role. If you are navigating expansive intricate business data terrains, a precise GPS comes in handy, right? That is precisely what data lineage offers in BI.
The driving concept is simple; data lineage illuminates how data moves through the business systems, serving as a blueprint for your data’s journey. It trails each festering data element, from data sourcing, extraction, and transformation to the eventually loaded business intelligence data.
Data lineage in BI is just like a detective operation, uncovering the layered, complex data puzzle by making the process transparent. Consequently, tracing errors and identifying their root cause becomes manageable. It thus removes uncertainties in the data interpretation, leading to confident data-driven decisions.
How Data Lineage Improves the Decision-Making Process
If you are at a crossroad and you have your GPS directing you, its accuracy will instill confidence in your decision to take the next turn, right? That’s the same confidence Data Lineage instills in decision-making.
Businesses primarily run on decisions. Suppose these decisions are manifested from inaccurate data, *insert catastrophic consequences here*. Data lineage takes the reigns in enhancing decision-making precision. It provides a clear path that data follows, ensuring validating the data’s integrity becomes seamlessly straightforward.
When data scientists and analysts understand the origins, transformations, and interactions of their data variables, they develop confidence in the results generated. As a result, the businesses’ strategic and operational decisions made on these data insights carry that confidence. How about that for the decision-making process!
Customer Story: Leveraging Data Lineage in Business Intelligence
Let’s look at a practical case: A global consumer goods company looking to improve sales and inventory management. The company invested in data lineage tools to track their data from the myriad of transactional data sources to their BI systems and dashboards.
The result? They discovered some crucial transformation errors occurring midway, causing inaccuracies in their projected inventory levels. Additionally, decision-makers got enlightened on the effects of promotional sales on their supply chain data. Transparency on these data connections allowed them to rectify the mistakes and yield correct inventory levels.
By leveraging data lineage, they achieved not only data accuracy and integrity, but also significant savings from efficient inventory management. The business intelligence effectively streamlined their decisions, revealing why a squeaky-clean data lineage approach in BI is essential for optimization and problem-solving.

Data Lineage and Data Quality: An Inseparable Pair
- Unearth the tactful understanding of data quality
- Discover how data lineage deeply influences data quality
- A practical case study expounding data quality enhancement with data lineage
Understanding Data Quality
Data quality, simply put, is the degree of excellence in data. The richest, most insightful datasets can become useless if they lack quality. High-quality data means it’s accurate, complete, consistent, reliable, and timely.
In a business context, poor data quality can result in significant operational and financial consequences. It can lead to incorrect decision-making, efficiency loss, and heighten compliance risks. Understanding data quality isn’t a luxury; it’s a necessity. Inaccurate data leads to misguided insights, impeding business growth. Therefore, maintaining high data quality should be a top priority, emerging as a cornerstone in successful business strategizing.
The Impact of Data Lineage on Data Quality
Data lineage displays the journey of data from its inception to its current position, highlighting its transformative phases. It’s like a roadmap for your data, marking every stop it made along its journey, providing crucial transparency for data tracking and governance.
A strong data lineage enhances data quality in multiple ways. First, it provides clear visibility into how data is transformed throughout its lifecycle. This understanding can help identify anomalies or areas where data quality may be compromised.
Second, data lineage facilitates the compliance process. Regulatory bodies demand high data standards. Data lineage delivers comprehensive insights into the data’s life cycle, laying the groundwork for excellent auditability. Errors or inconsistencies can be pinpointed and rectified, driving quality across data sets.
Customer Story: Enhancing Data Quality with Data Lineage
Consider a financial institution that collects and processes vast amounts of data daily. Initially, the firm grappled with inconsistencies and inaccuracies in its data, affecting its business analytics and decision-making process.
By implementing an effective data lineage program, the firm managed to trace problematic data back to its origin, uncovering where the inconsistencies began. They could rectify inaccurate transformations, greatly enhancing their data quality.
Combining these measures resulted in significant operational improvements. The firm’s decision-making process became more accurate, significantly reducing the risk of incorrect data-driven decisions. This case study underlines the profound impact that data lineage can have on ensuring data quality.
Despite the challenges, the power of effectively unifying data lineage and data quality cannot be undermined. Embracing this inseparable pair paves the way for business intelligence, compliance, and overall operational excellence.
Discovering Data's Past: A Journey's End, A New Beginning
Knowledge of data lineage is power. You’ve explored how tracing data’s origin and transformation brings clarity to business decisions. It’s key to ensuring security, enhancing quality, and fulfilling regulatory compliance.
And what’s the wealth that you’ve dug out from this expedition? It’s not just piles of data, but valuable narratives lying beneath every byte and bit – your data’s lineage.
Nudge this newfound understanding into action. Test the waters with a data lineage tool. Look at your business’s data landscapes and put down digital footprints of data’s journey. Remember, every piece of information you field has a story. Unearth it. Listen to it.
So, think for a moment: How well do you know your data’s journey? Are you letting precious informational gold slip away untracked?
Therein lies the thrill of the chase. In every bit of data explored, there’s more to discover. This isn’t merely the end of a blog post—it’s the starting point for your own data lineage adventure. Dive in. The data ocean awaits.